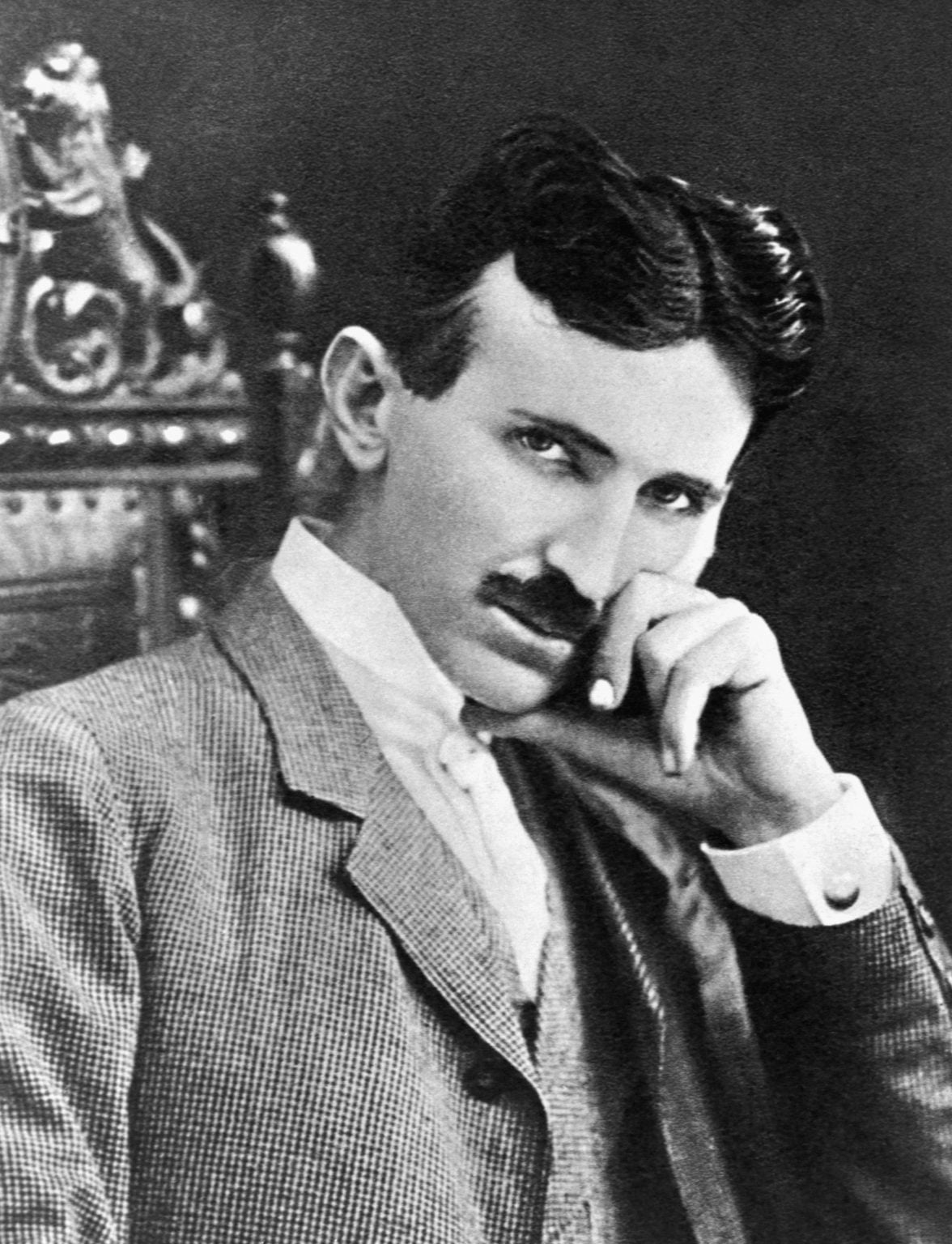
By the end of his brilliant and tortured life, the Serbian physicist, engineer and inventor Nikola Tesla was penniless and living in a small New York City hotel room. He spent days in a park surrounded by the creatures that mattered most to him—pigeons—and his sleepless nights working over mathematical equations and scientific problems in his head. That habit would confound scientists and scholars for decades after he died, in 1943. His inventions were designed and perfected in his imagination.
Tesla believed his mind to be without equal, and he wasn’t above chiding his contemporaries, such as Thomas Edison, who once hired him. “If Edison had a needle to find in a haystack,” Tesla once wrote, “he would proceed at once with the diligence of the bee to examine straw after straw until he found the object of his search. I was a sorry witness of such doing that a little theory and calculation would have saved him ninety percent of his labor.”
But what his contemporaries may have been lacking in scientific talent (by Tesla’s estimation), men like Edison and George Westinghouse clearly possessed the one trait that Tesla did not—a mind for business. And in the last days of America’s Gilded Age, Nikola Tesla made a dramatic attempt to change the future of communications and power transmission around the world. He managed to convince J.P. Morgan that he was on the verge of a breakthrough, and the financier gave Tesla more than $150,000 to fund what would become a gigantic, futuristic and startling tower in the middle of Long Island, New York. In 1898, as Tesla’s plans to create a worldwide wireless transmission system became known, Wardenclyffe Tower would be Tesla’s last chance to claim the recognition and wealth that had always escaped him.
Nikola Tesla was born in modern-day Croatia in 1856; his father, Milutin, was a priest of the Serbian Orthodox Church. From an early age, he demonstrated the obsessiveness that would puzzle and amuse those around him. He could memorize entire books and store logarithmic tables in his brain. He picked up languages easily, and he could work through days and nights on only a few hours sleep.
At the age of 19, he was studying electrical engineering at the Polytechnic Institute at Graz in Austria, where he quickly established himself as a star student. He found himself in an ongoing debate with a professor over perceived design flaws in the direct-current (DC) motors that were being demonstrated in class. “In attacking the problem again I almost regretted that the struggle was soon to end,” Tesla later wrote. “I had so much energy to spare. When I undertook the task it was not with a resolve such as men often make. With me it was a sacred vow, a question of life and death. I knew that I would perish if I failed. Now I felt that the battle was won. Back in the deep recesses of the brain was the solution, but I could not yet give it outward expression.”
He would spend the next six years of his life “thinking” about electromagnetic fields and a hypothetical motor powered by alternate-current that would and should work. The thoughts obsessed him, and he was unable to focus on his schoolwork. Professors at the university warned Tesla’s father that the young scholar’s working and sleeping habits were killing him. But rather than finish his studies, Tesla became a gambling addict, lost all his tuition money, dropped out of school and suffered a nervous breakdown. It would not be his last.
In 1881, Tesla moved to Budapest, after recovering from his breakdown, and he was walking through a park with a friend, reciting poetry, when a vision came to him. There in the park, with a stick, Tesla drew a crude diagram in the dirt—a motor using the principle of rotating magnetic fields created by two or more alternating currents. While AC electrification had been employed before, there would never be a practical, working motor run on alternating current until he invented his induction motor several years later.
In June 1884, Tesla sailed for New York City and arrived with four cents in his pocket and a letter of recommendation from Charles Batchelor—a former employer—to Thomas Edison, which was purported to say, “My Dear Edison: I know two great men and you are one of them. The other is this young man!”
A meeting was arranged, and once Tesla described the engineering work he was doing, Edison, though skeptical, hired him. According to Tesla, Edison offered him $50,000 if he could improve upon the DC generation plants Edison favored. Within a few months, Tesla informed the American inventor that he had indeed improved upon Edison’s motors. Edison, Tesla noted, refused to pay up. “When you become a full-fledged American, you will appreciate an American joke,” Edison told him.
Tesla promptly quit and took a job digging ditches. But it wasn’t long before word got out that Tesla’s AC motor was worth investing in, and the Western Union Company put Tesla to work in a lab not far from Edison’s office, where he designed AC power systems that are still used around the world. “The motors I built there,” Tesla said, “were exactly as I imagined them. I made no attempt to improve the design, but merely reproduced the pictures as they appeared to my vision, and the operation was always as I expected.”
Tesla patented his AC motors and power systems, which were said to be the most valuable inventions since the telephone. Soon, George Westinghouse, recognizing that Tesla’s designs might be just what he needed in his efforts to unseat Edison’s DC current, licensed his patents for $60,000 in stocks and cash and royalties based on how much electricity Westinghouse could sell. Ultimately, he won the “War of the Currents,” but at a steep cost in litigation and competition for both Westinghouse and Edison’s General Electric Company.
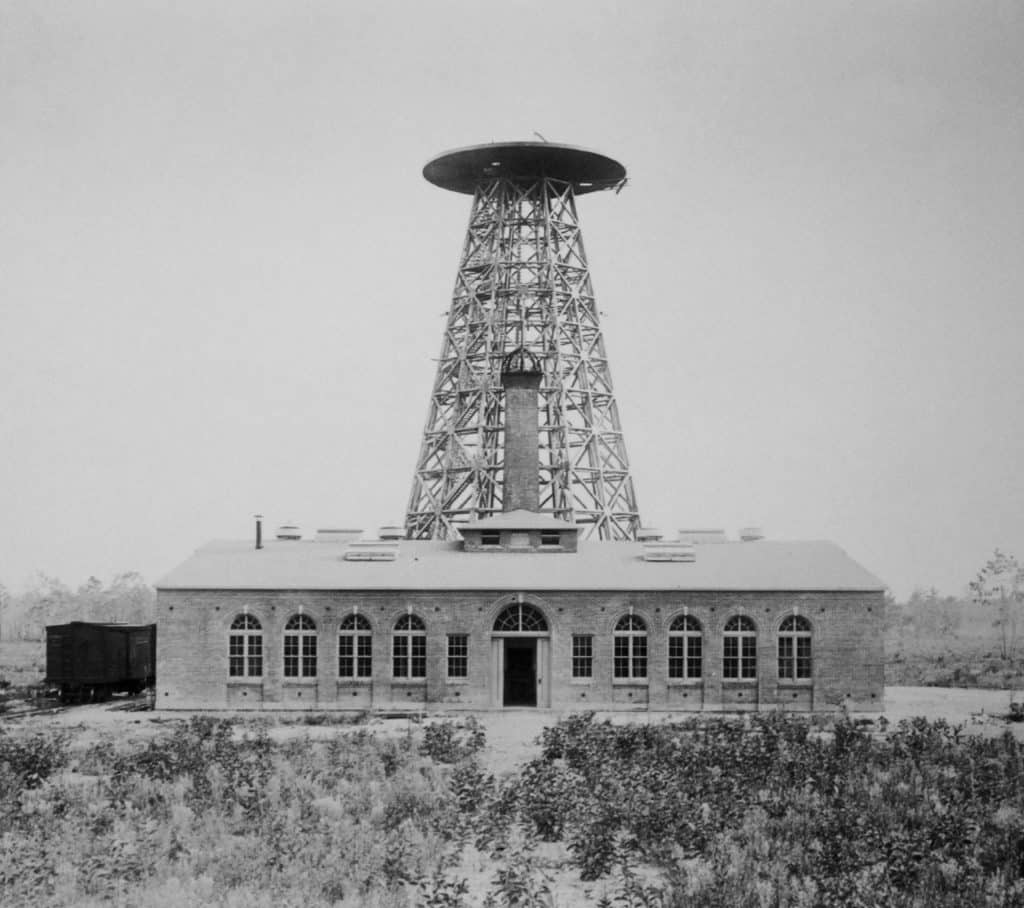

Fearing ruin, Westinghouse begged Tesla for relief from the royalties Westinghouse agreed to. “Your decision determines the fate of the Westinghouse Company,” he said. Tesla, grateful to the man who had never tried to swindle him, tore up the royalty contract, walking away from millions in royalties that he was already owed and billions that would have accrued in the future. He would have been one of the wealthiest men in the world—a titan of the Gilded Age.
His work with electricity reflected just one facet of his fertile mind.