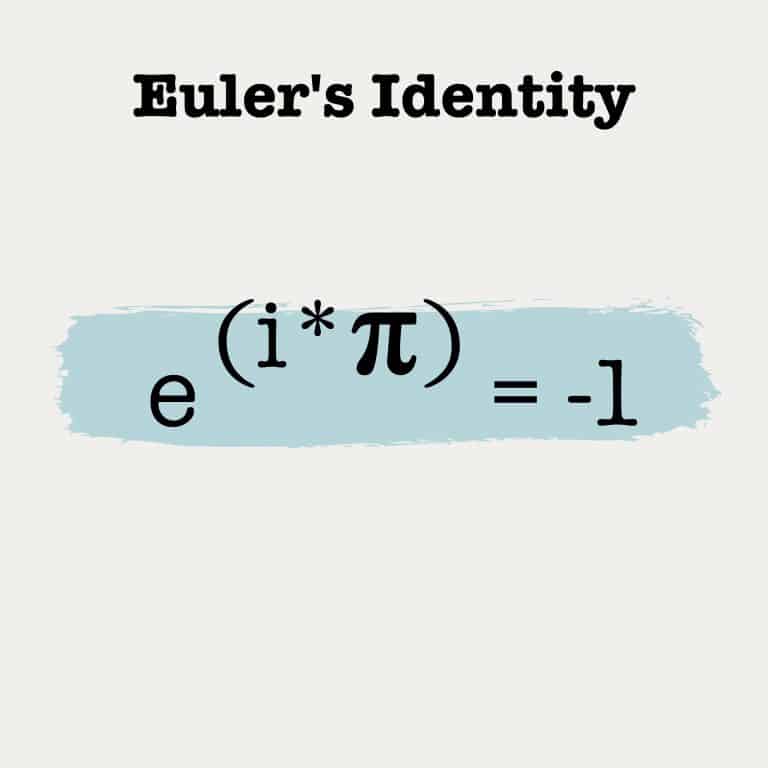
The imaginary unit, i, is a solution to the quadratic equation x^2 + 1 = 0, where (-1)^2 = 1 or x=√-1. It is called imaginary because there is no real number with this property. Imaginary numbers helped extend the real number system to the complex number system, in which at least one root for every nonconstant polynomial exists.

Boltzmann’s Constant
The fundamental constant of physics, the Boltzmann constant, is one of the seven "defining constants" that have been given exact definitions.